
(Image credit: Shutterstock)
Today, we'll put the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs the Intel Core Ultra 9 285K in a heated contest to see which chip comes out on top. The best processor is not necessarily the one with the most number of cores or the highest clock speeds; rather, it is the one that fulfills your specific requirements and fits within your budget. Gamers do not necessarily require the highest-end chip to enjoy the latest AAA games, although having one wouldn't hurt. However, numerous compelling reasons exist for a consumer to seek to acquire a flagship processor.
You may be part of a small, elite crowd of enthusiastic gamers with the financial capacity to acquire the latest and greatest mainstream processor. Alternatively, you could be among the type of users who use their systems for more than just casual gaming, thereby warranting a more substantial investment in a processor that provides considerable processing power alongside exceptional gaming performance. The million-dollar question remains whether to choose between Intel or AMD, as both chipmakers have released highly compelling flagship processors in the current market.
AMD currently has two coexisting mainstream processor lineups in the retail market. The vanilla Ryzen 9000 (codename Granite Ridge) series was the inaugural launch, later followed by the Ryzen 9000X3D series, which incorporates AMD's 3D V-Cache technology, significantly enhancing gaming performance. Consequently, AMD has two flagship products: the Ryzen 9 9950X3D from the 3D V-Cache branch and the Ryzen 9 9950X from the main family. In contrast, Intel only has the Core Ultra 200S (codenamed Arrow Lake) series to compete against AMD, with the Core Ultra 9 285K as the singular leader of Intel's army.
Features and Specifications: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D features Zen 5 execution cores and adheres to a conventional 16-core, 32-thread configuration. On the contrary, the Core Ultra 9 285K employs a hybrid design, integrating P-cores (Lion Cove) and E-cores (Skymont). Consequently, the Core Ultra 9 285K showcases a 24-core, 24-thread design. With Arrow Lake, Intel went with an approach without Hyper-Threading, so the Core Ultra 9 285K has fewer threads than the Ryzen 9 9950X3D.
Concerning clock speeds, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D exhibits a 16% greater base clock speed than the Core Ultra 9 285K. However, both processors possess identical boost clocks. For cache capacity, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D is equipped with AMD's 3D V-Cache, providing a total cache of 144MB (16MB L2 + 128MB L3). On the other hand, the Core Ultra 9 285K is accompanied by a cache capacity of 76MB (36MB L2 + 40MB L3). Consequently, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has 3.2X more L3 cache, which is advantageous for gaming and specific workloads.
Processor | AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D | Intel Core Ultra 9 285K |
|---|---|---|
MSRP | $699 | $599 |
Microarchitecture | Zen 5 X3D | Lion Cove / Skymont |
Cores / Threads (P+E) | 16 / 32 | 24 / 24 (8+16) |
P-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | 4.3 / 5.7 | 3.7 / 5.7 |
E-Core Base / Boost Clock (GHz) | N/A | 3.2 / 4.6 |
Cache (L2/L3) | 144MB (16+128) | 76MB (36+40) |
TDP / PBP or MTP | 170W / 230W | 125W / 250W |
Memory | DDR5-5600 | CUDIMM DDR5-6400 / DDR5-5600 |
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D has a 36% greater TDP (Thermal Design Power) or, in Intel's case, PBP (Processor Base Power), than the Core Ultra 9 285K. Nevertheless, the latter features a 9% higher MTP (Maximum Turbo Power). Therefore, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has superior power efficiency to the Core Ultra 9 285K.
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D and Core Ultra 9 285K support PCIe 5.0 connectivity and DDR5 memory. Both provide 24 high-speed PCIe 5.0 lanes to support the latest graphics cards and PCIe 5.0 SSDs. Regarding memory support, only the Core Ultra 9 285K has embraced CUDIMMs (Clocked Unbuffered Dual In-line Memory Modules), bumping the native supported frequency up to DDR5-6400. As far as conventional DIMMs are concerned, both support DDR5-5600.
Platform longevity favors the Ryzen 9 9950X3D, as the chip resides on the AM5 platform, which was launched in 2022 with AMD's commitment to providing support until 2027. On the other hand, the Core Ultra 9 285K uses the LGA1851 platform, which was released in 2024, but its life span is likely to be limited. There are indications that Intel may refresh Arrow Lake for LGA1851 before transitioning to the LGA1954 platform for forthcoming processors.
⭐ Winner: Tie
Specification-wise, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has a big L3 cache thanks to AMD's 3D V-Cache technology and lower power consumption overall than the Core Ultra 9 285K. Another of AMD's strengths is the life expectancy of the AM5 platform, which is substantially higher than LGA1851. Investing in the platform now offers a ticket for future processor upgrades.
The LGA1851, in contrast, represents a fading platform. Arrow Lake may be the sole chip to utilize the LGA1851 platform, or possibly Arrow Lake Refresh, assuming the latest rumors are true. This is not particularly surprising, as the typical cadence for Intel sockets has consistently been two or three generations of chips, unlike AMD.
In LGA1851's defense, it is presently the sole platform that completely supports CUDIMMs. One advantage the Core Ultra 9 285K holds over the Ryzen 9 9950X3D is the possibility of leveraging CUDIMMs, such as high-speed memory DDR5-9200 and beyond. Nevertheless, considering the long life span of AM5, it is likely that full CUDIMM support will be introduced for AMD's platform in due course.
Gaming Benchmarks and Performance: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
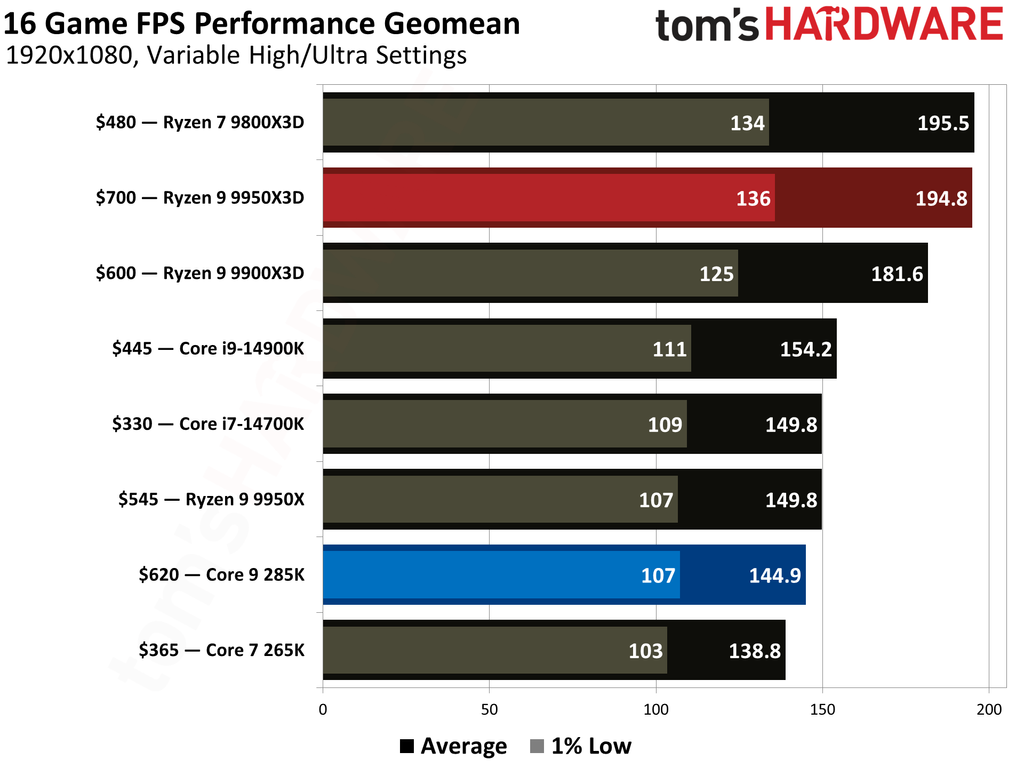
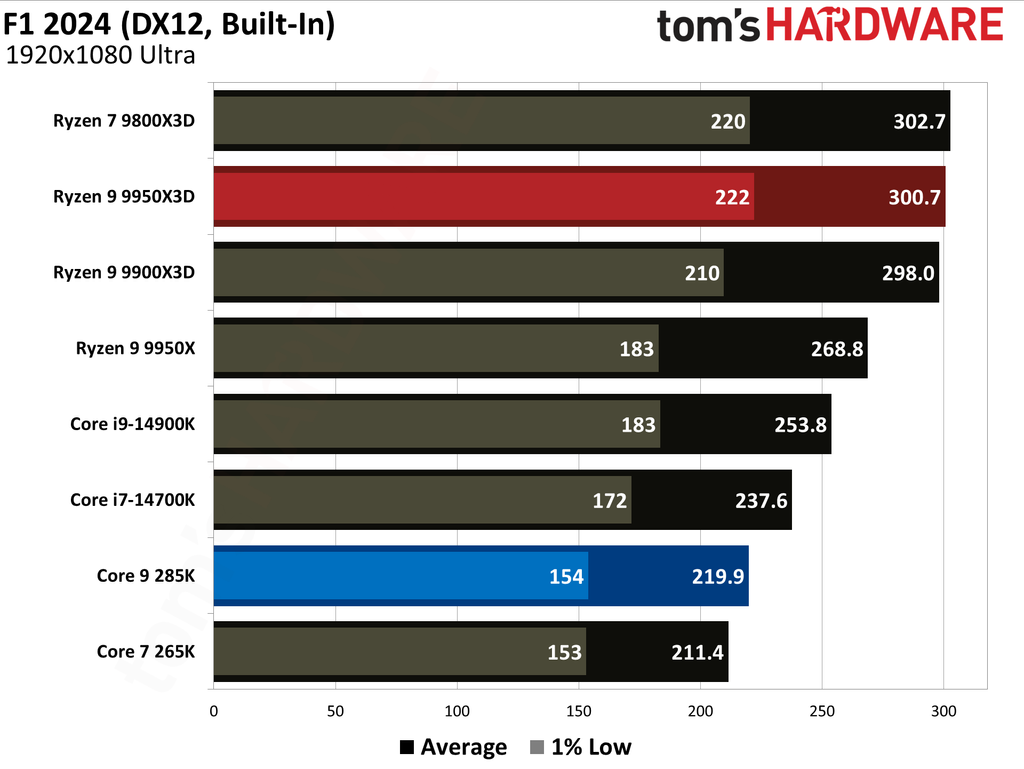
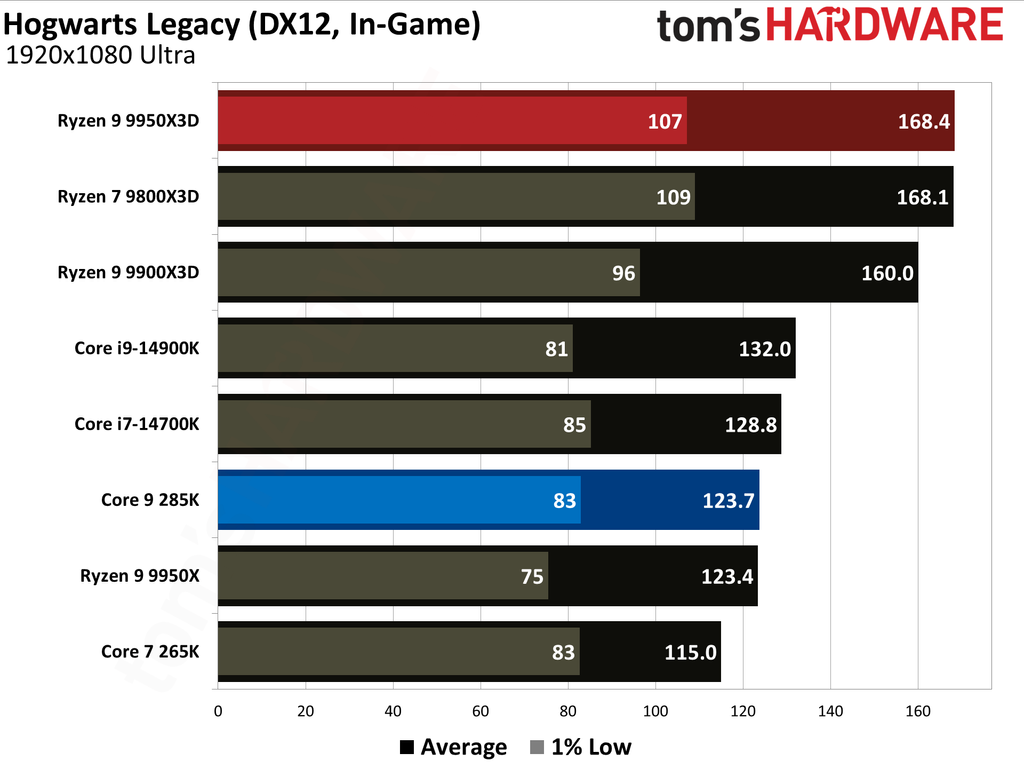
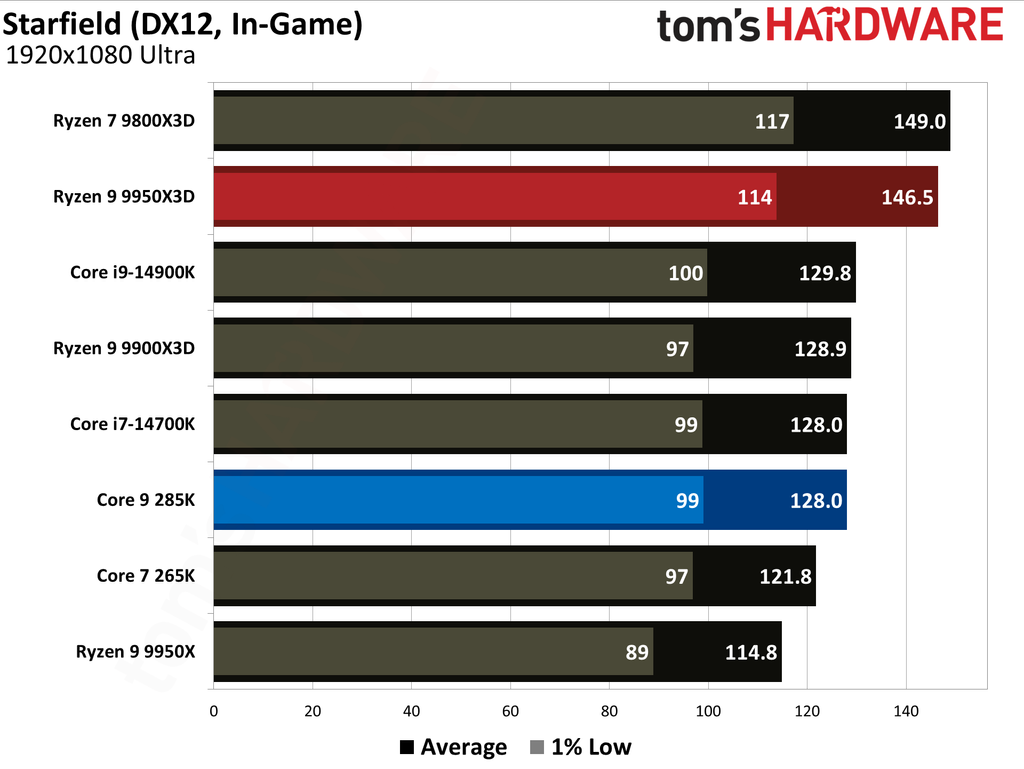
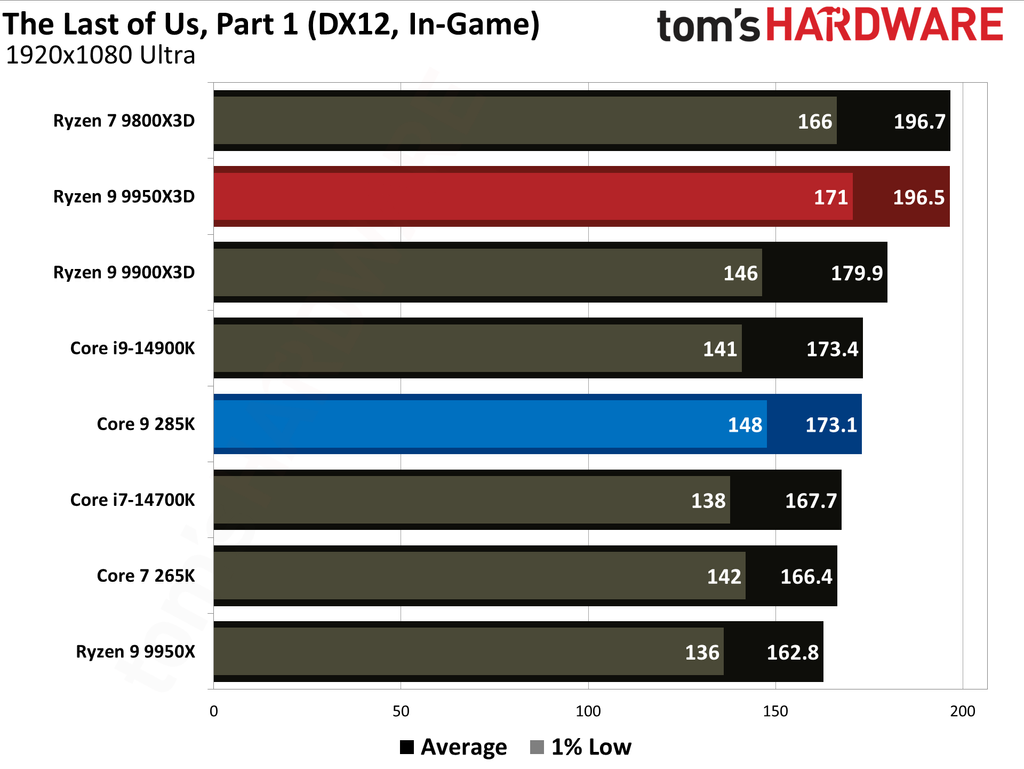
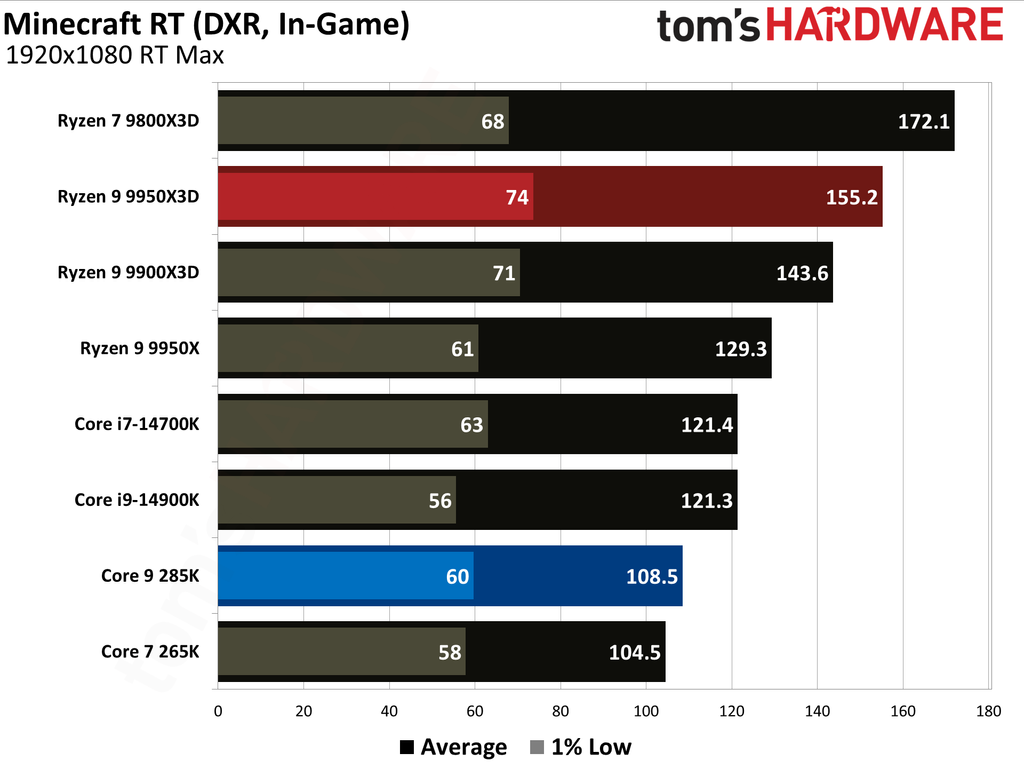
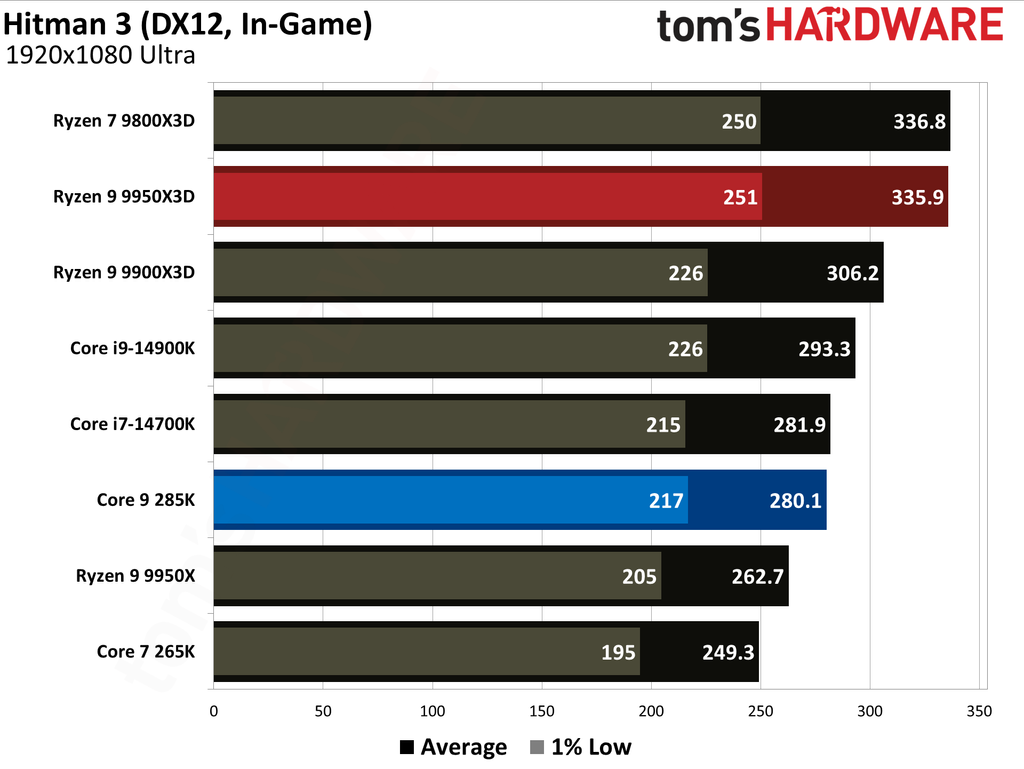
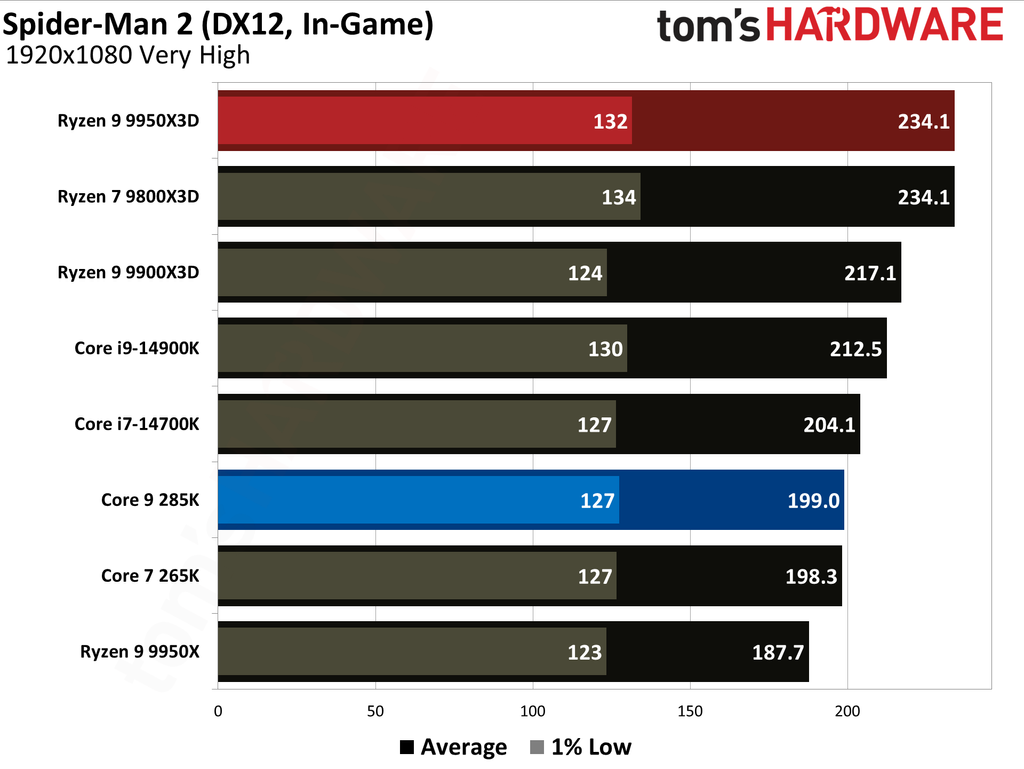
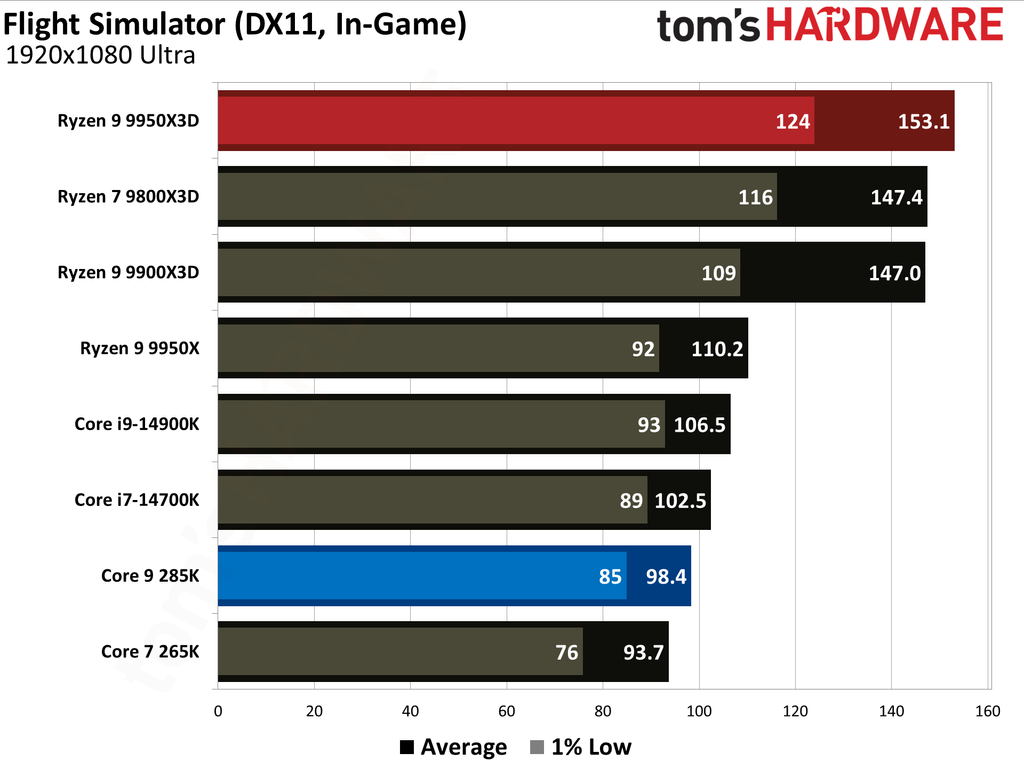
This article provides an overview of the Ryzen 9 9950X3D and Core Ultra 9 285K's performance metrics. We have also published in-depth individual reviews of these two CPUs, which you can refer to for more details. These graphs show the geometric mean of our gaming test results with these two CPUs at 1080p (1920x1080) resolution.
We paired both CPUs with the Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 graphics card to minimize potential bottlenecks. Testing at 1080p might seem irrelevant for such a powerful setup, but this resolution allows us to see the full potential of our CPUs in gaming.
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
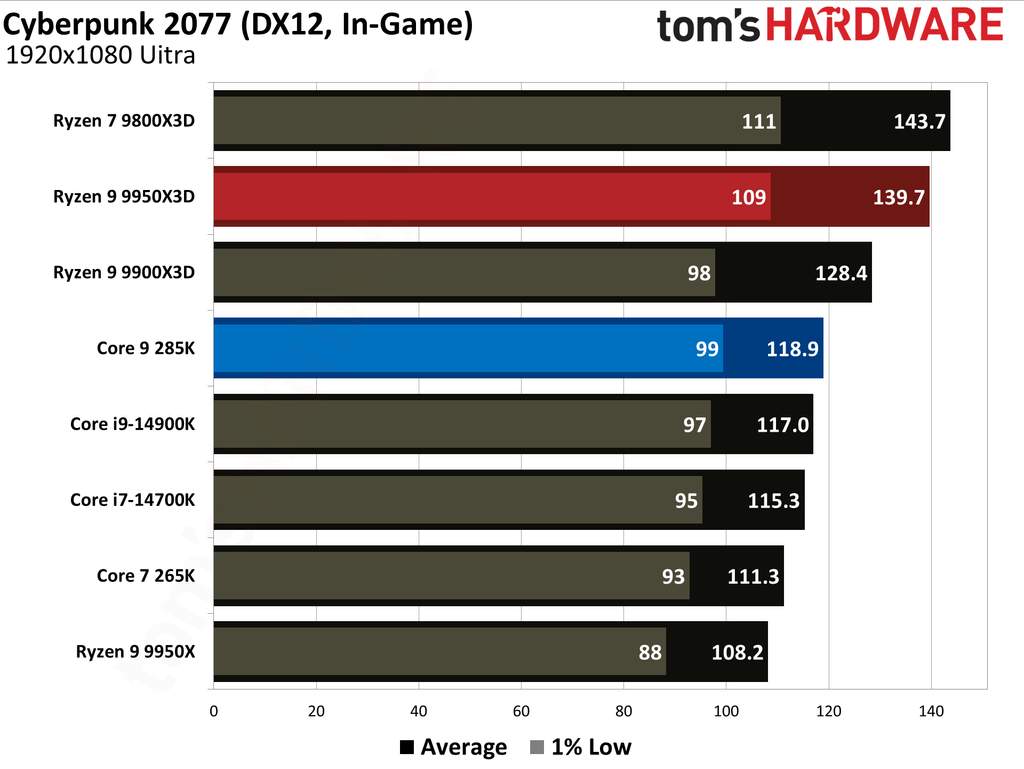
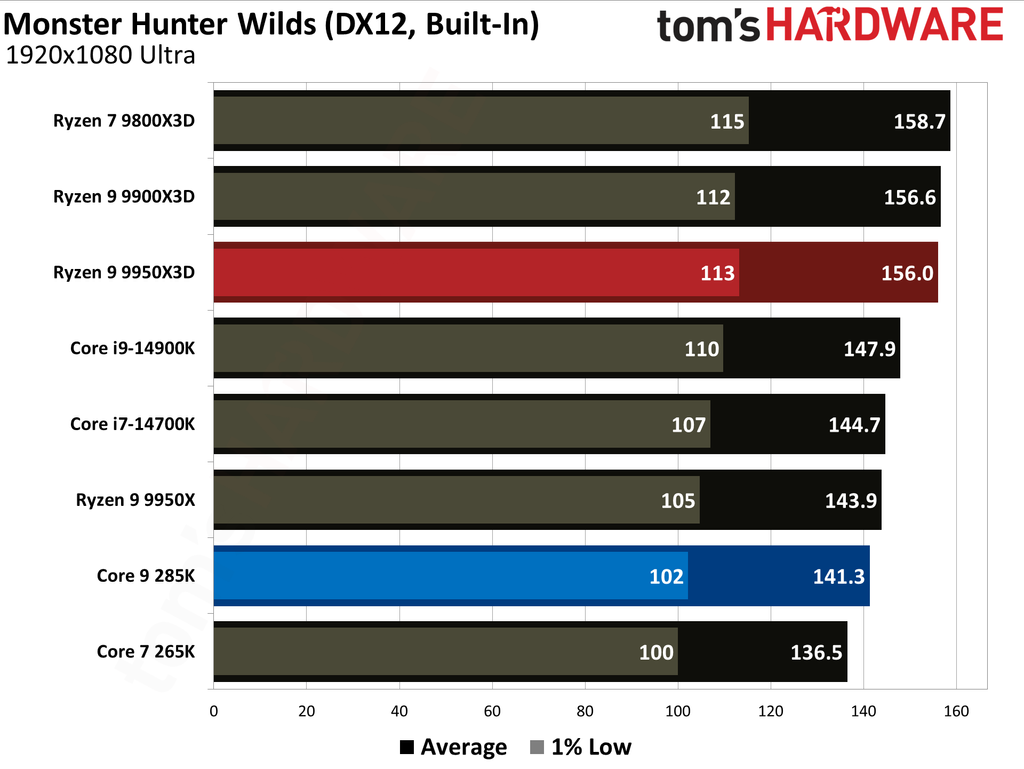
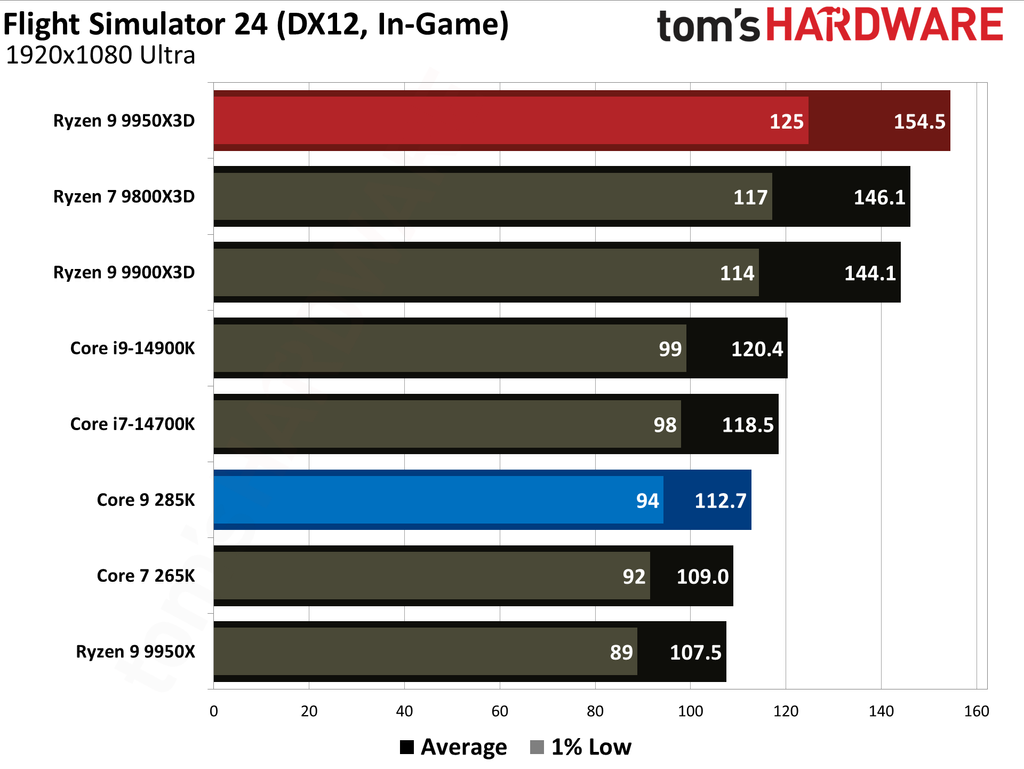
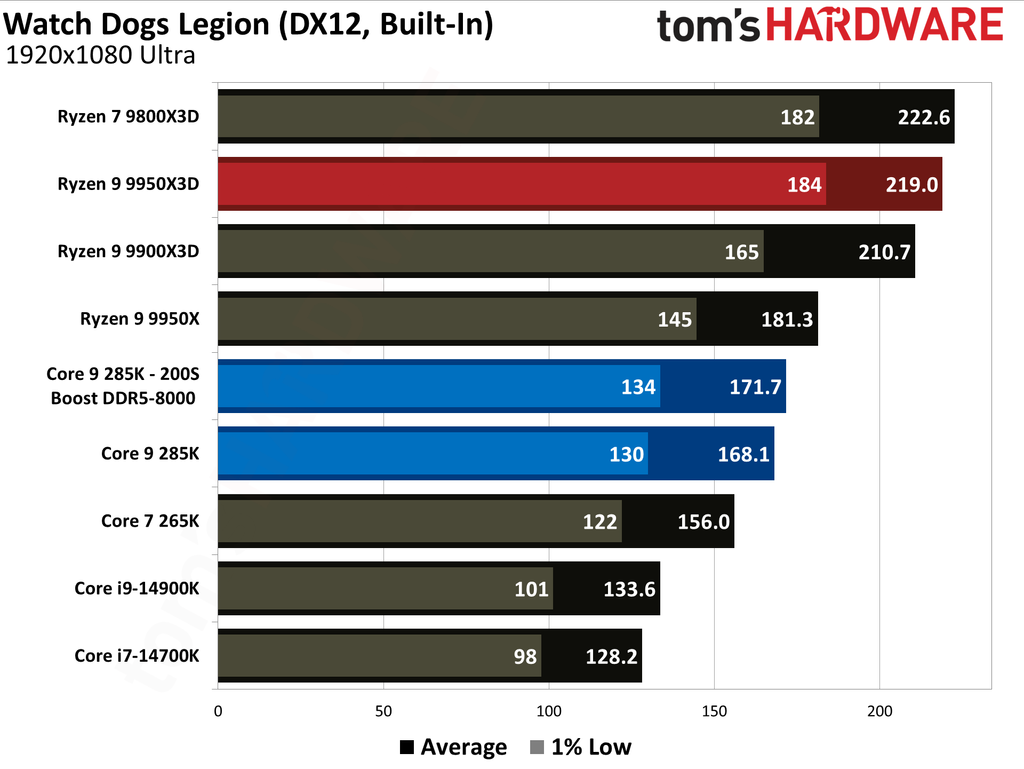
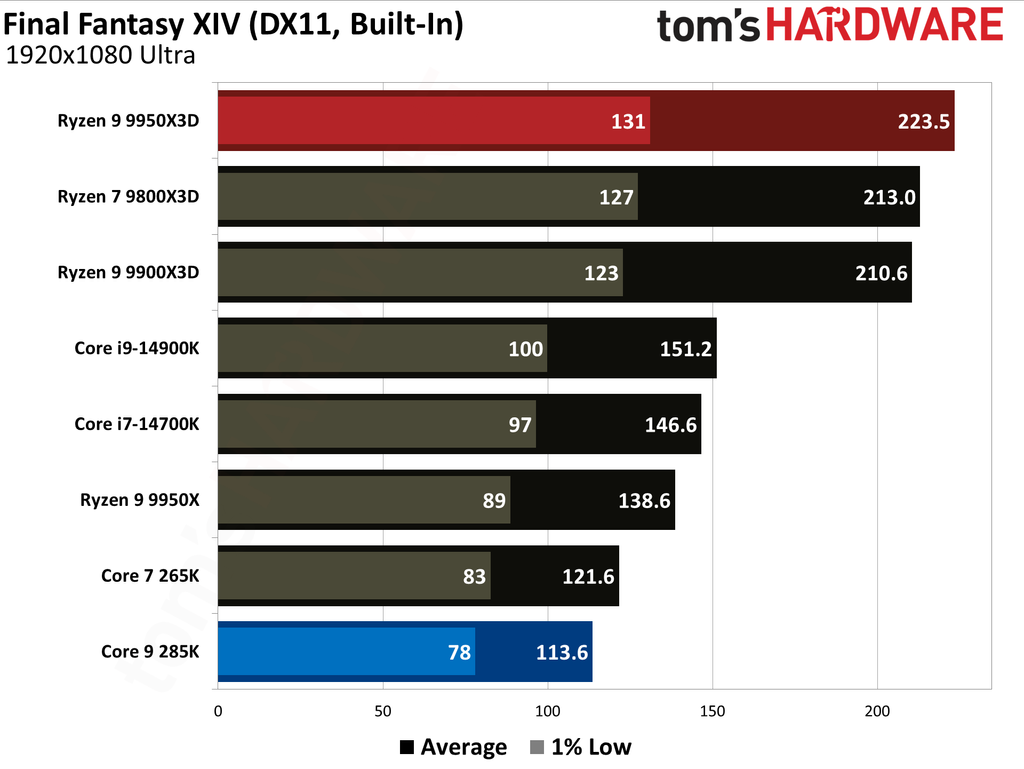
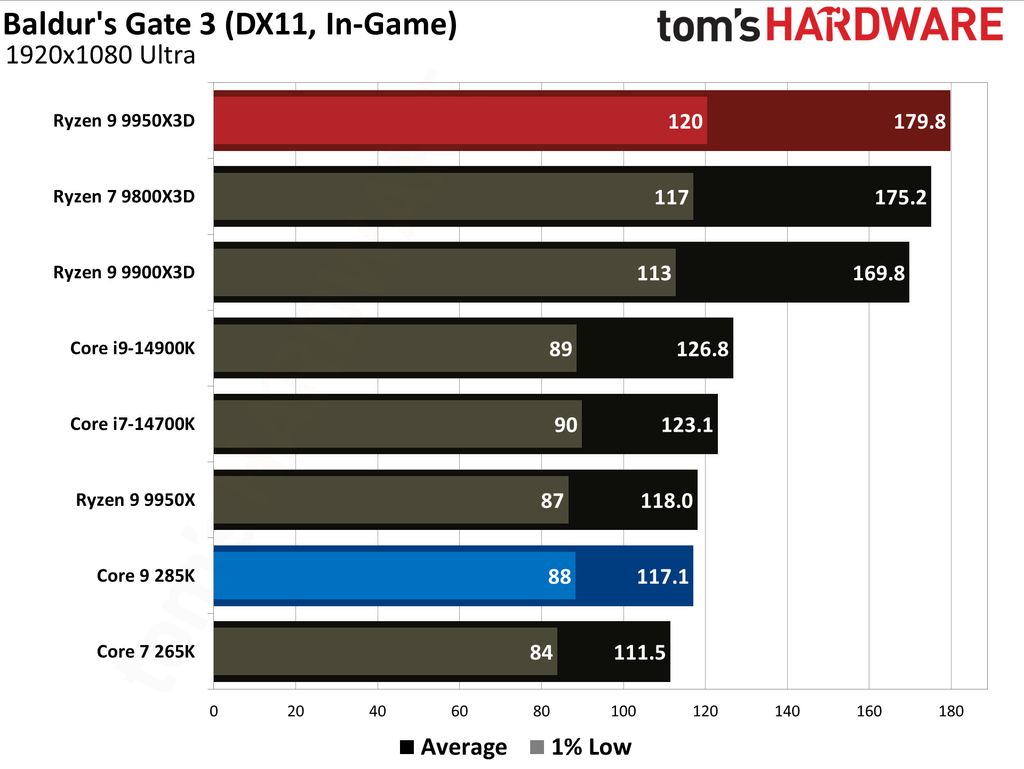
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D outperformed the Core Ultra 9 285K in gaming performance. This outcome was anticipated, as gaming performance is the former's most notable strength, attributable to the substantial L3 cache enabled by AMD's 3D V-Cache technology.
Cumulatively, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D yielded average frame rates that were 34% higher than those of the Core Ultra 9 285K throughout our testing suite of 16 games, utilizing a combination of High and Ultra graphical settings at 1080p. Furthermore, the AMD flagship demonstrated a 27% higher result in 1% Lows.
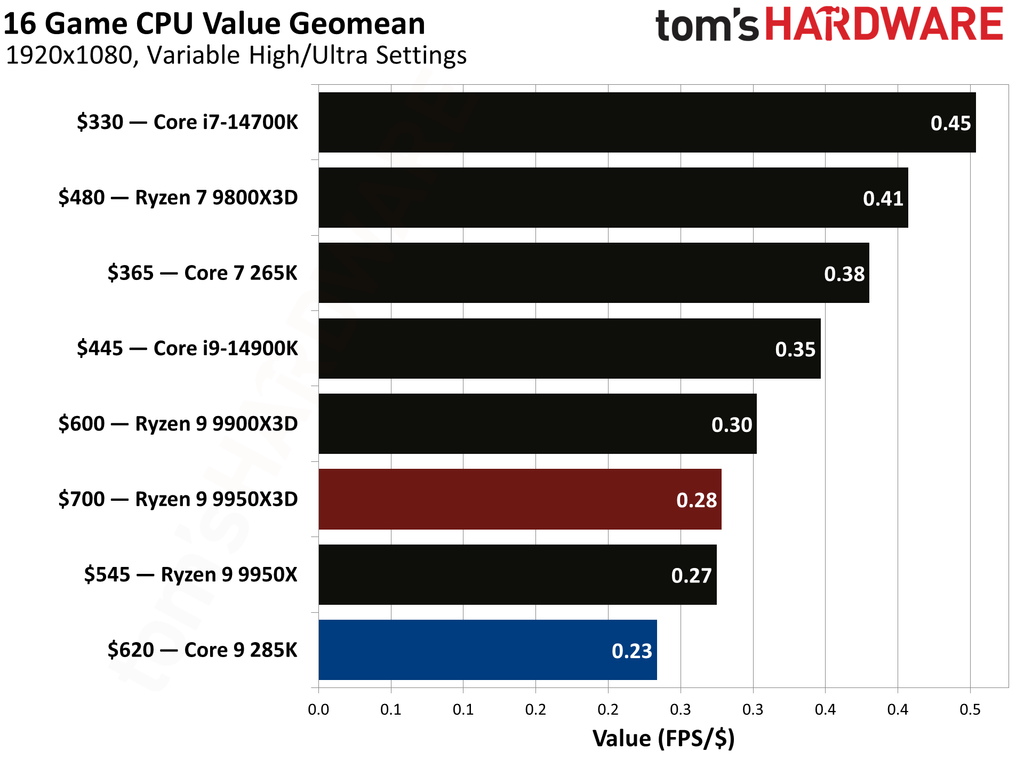
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D and Core Ultra 9 285K hit the market at $699 and $620, respectively. The former presents 0.28 FPS per dollar, while the latter offers 0.23. Despite costing 13% more, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has more gaming value for your money. While the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has maintained its pricing, the Core Ultra 9 285K has dropped to $589, reaching 0.25.
⭐ Winner: AMD
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D is undoubtedly the better choice for gaming enthusiasts. While the Core Ultra 9 285K is a capable gaming processor, it falls short compared to the Ryzen 9 9950X3D, which is almost 35% faster in average frame rates and close to 30% faster in 1% Lows.
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D has consistently maintained a higher price point than the Core Ultra 9 285K. Notwithstanding the recent price reductions of the Core Ultra 9 285K, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D continues to provide better value in gaming.
Productivity Performance: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
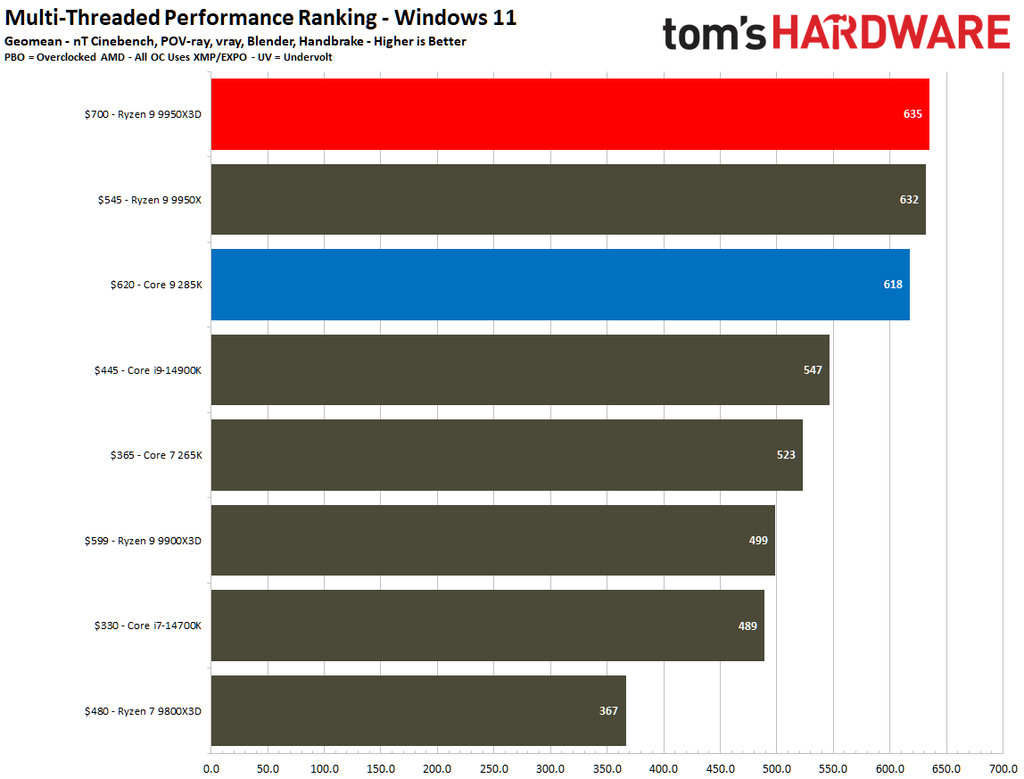
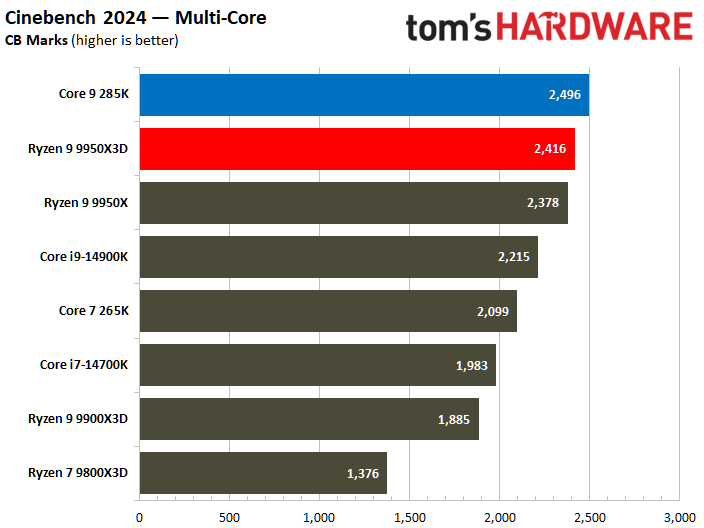
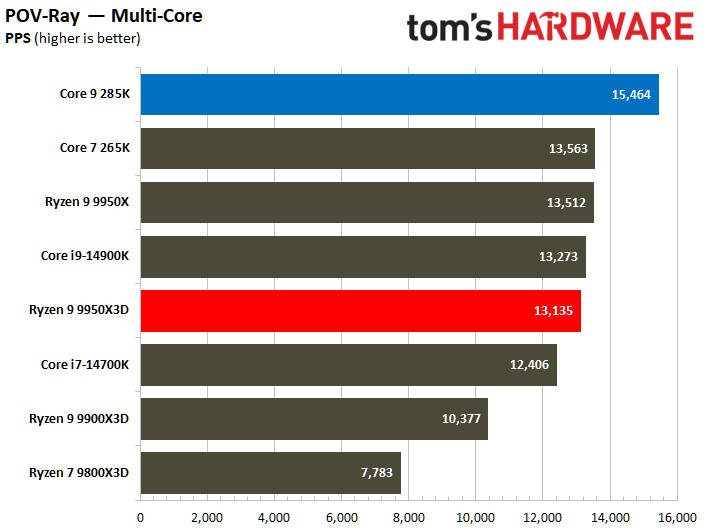
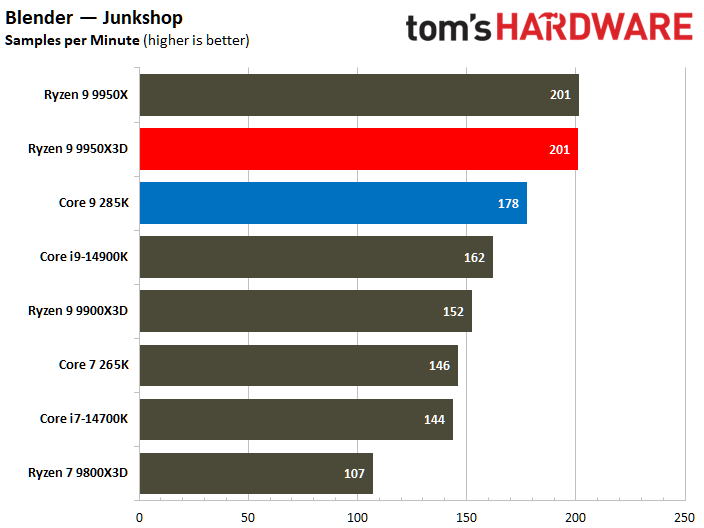
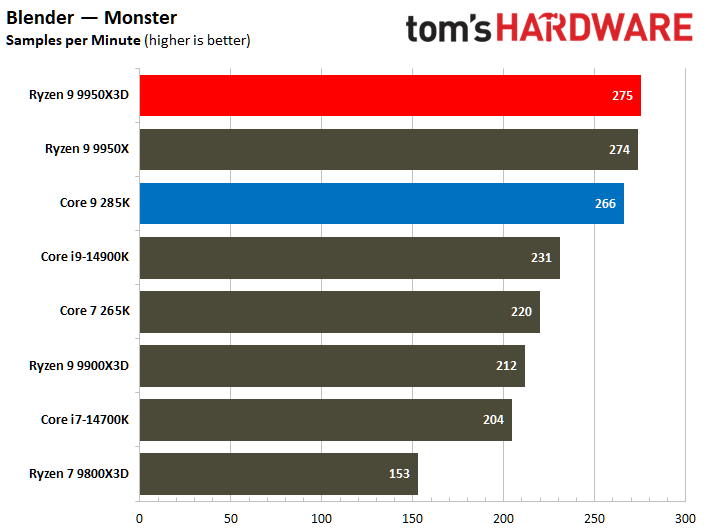
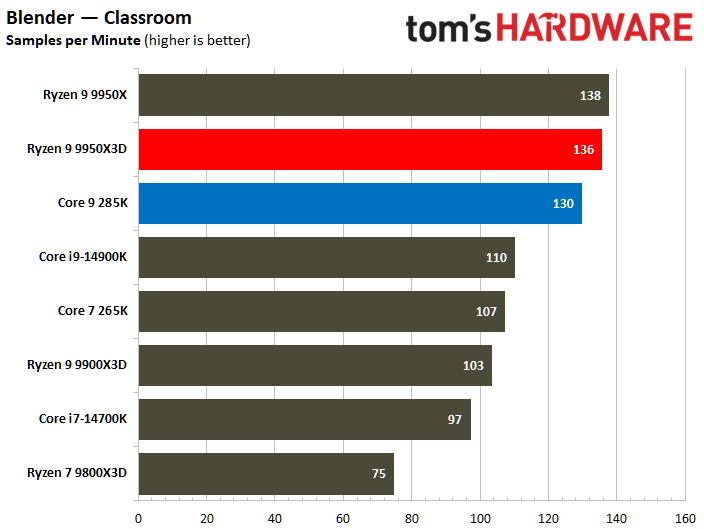
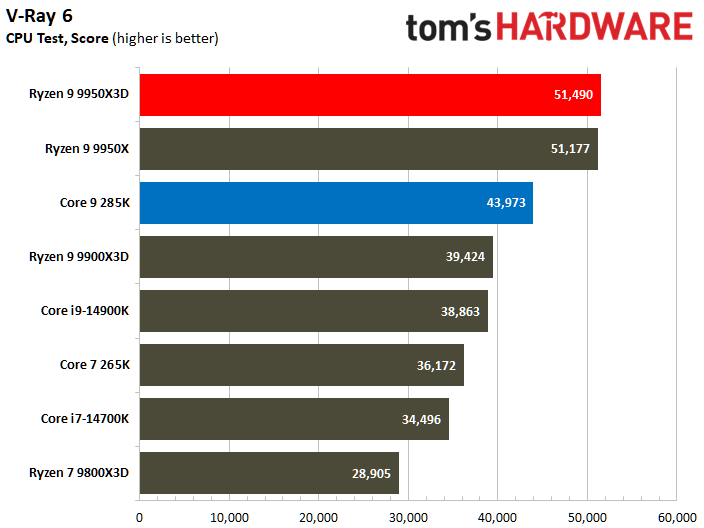
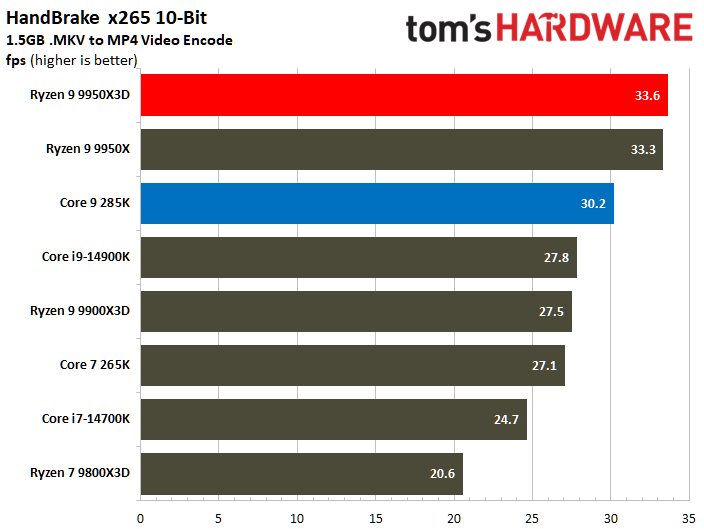
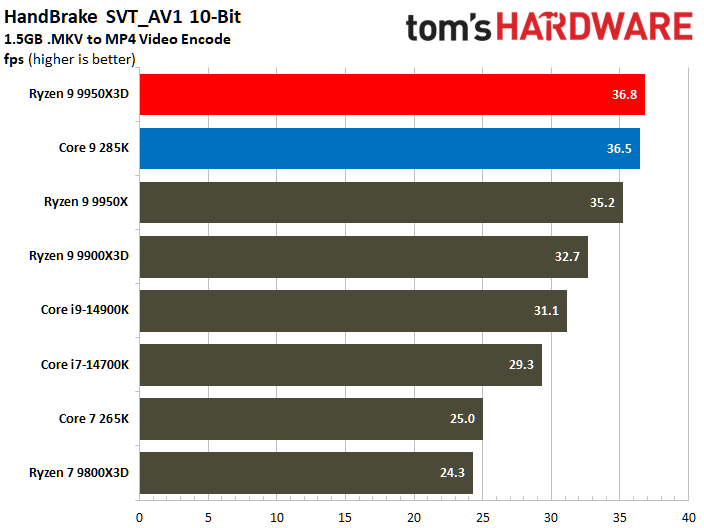
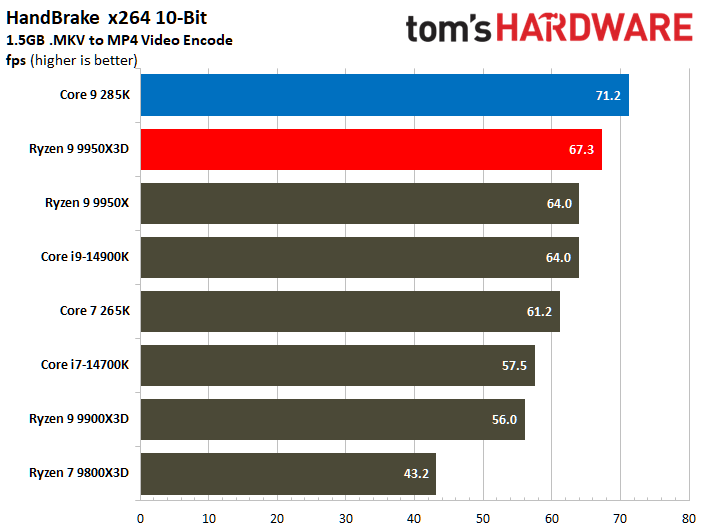
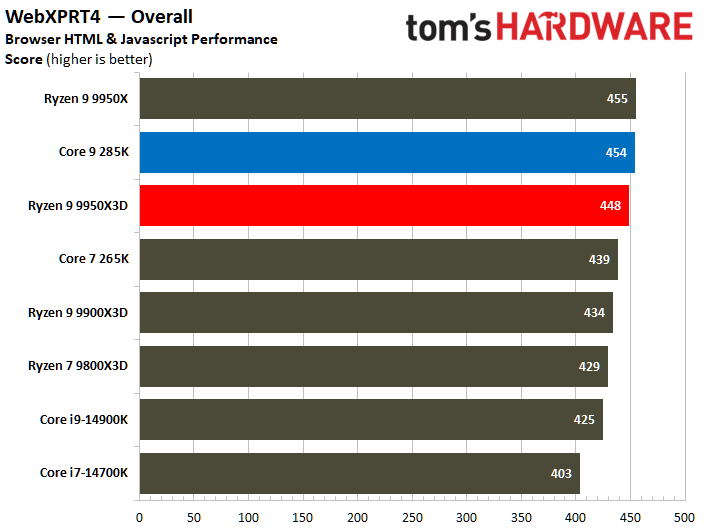
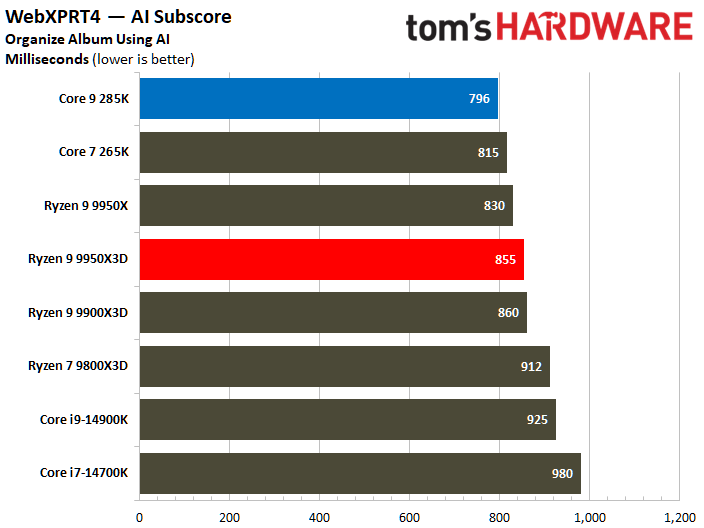
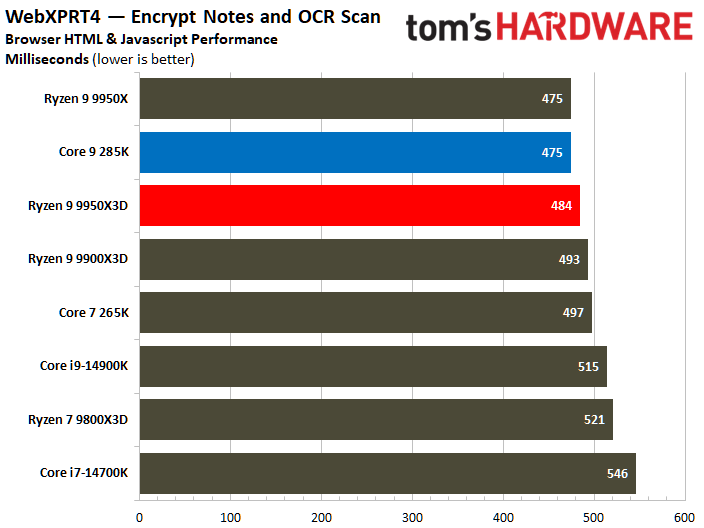
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D flaunts superior multi-threaded performance, but the contest is heated. The Zen 5 processor delivers a mere 3% higher multi-threaded performance than the Core Ultra 9 285K.
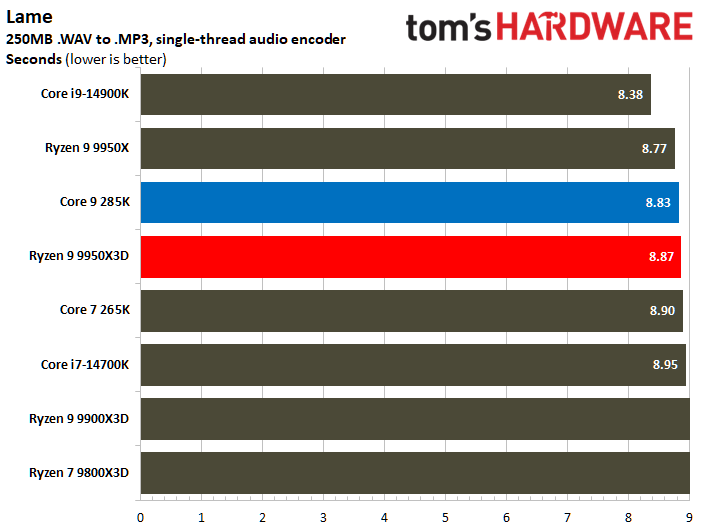
Looking at benchmarks individually, there are times when the Core Ultra 9 285K is substantially faster. For example, the Intel chip boasted 18% higher results in POV-Ray or 11% higher in HandBrake x265. The Ryzen 9 9950X3D also has its moments, such as in V-Ray 6, where it outperformed the Core Ultra 9 285K by 17%.
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
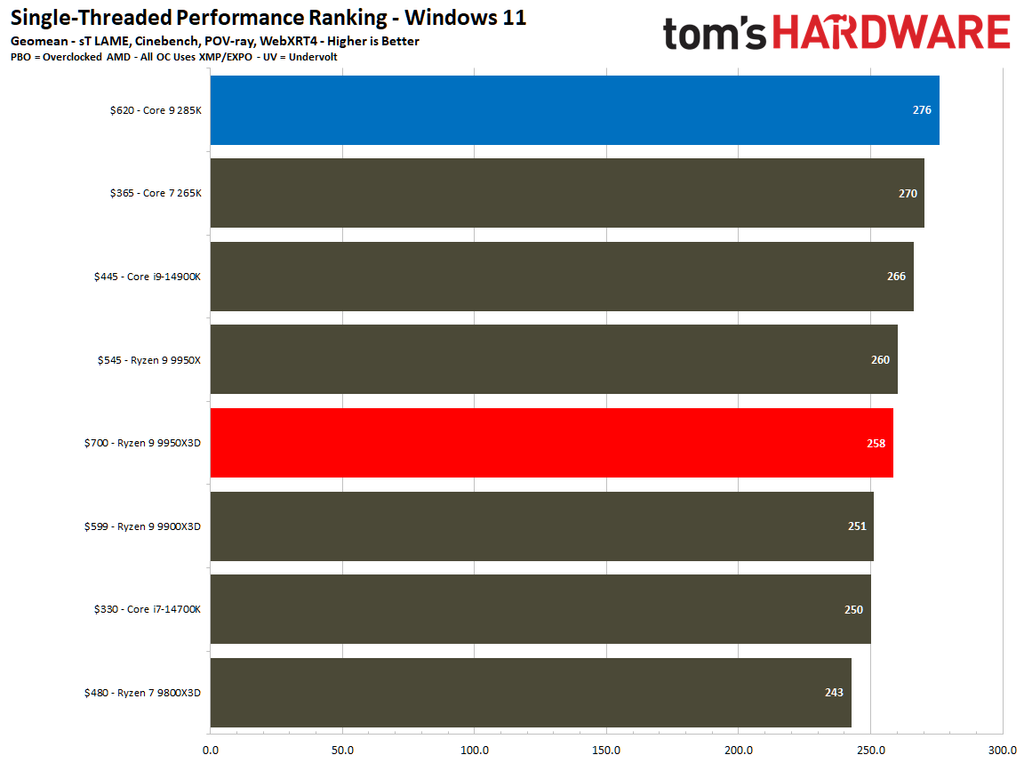
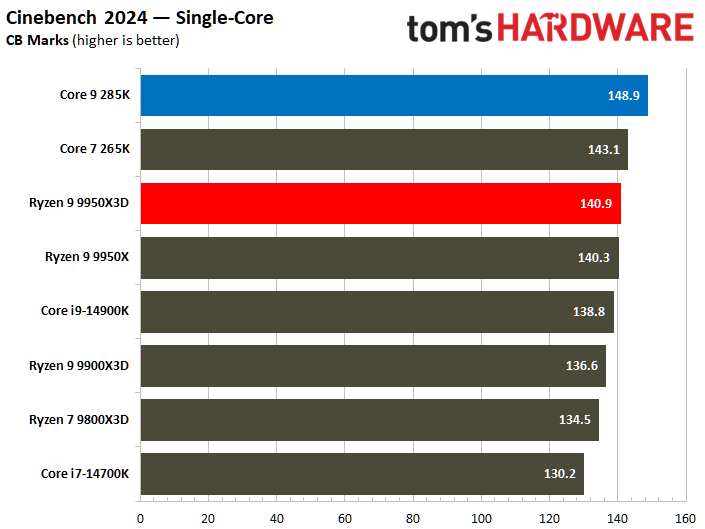
Intel continues to be the leader in single-threaded performance; however, the disparity has been narrowing, as evidenced by the current generation. The Core Ultra 9 285K achieved a 9% better single-threaded overall than the Ryzen 9 9950X3D.
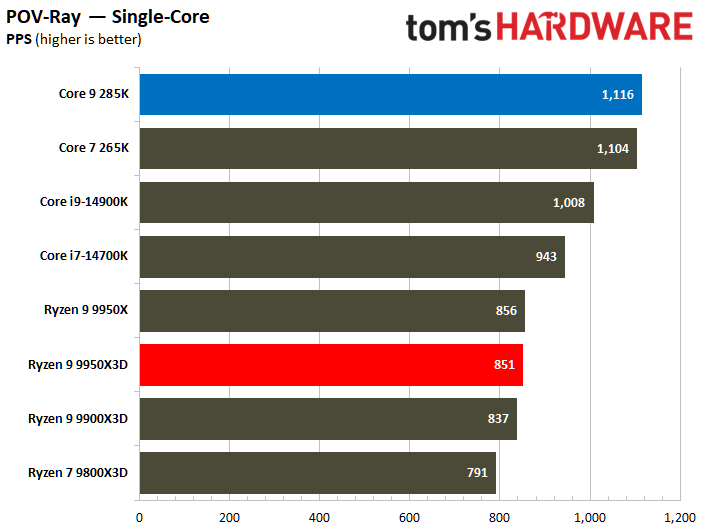
The POV-Ray benchmark clearly favors the Core Ultra 9 285K, which significantly surpassed the Ryzen 9 9950X3D by an impressive 31%. Conversely, the performance delta between the two processors wasn't as big in other workloads.
⭐ Winner: Tie
There is no definitive victor in this comparison. The Ryzen 9 9950X3D has higher multi-threaded performance relative to the Core Ultra 9 285K. Nevertheless, the disparity stands at merely 3%, a difference that may not be noteworthy across all workloads.
Meanwhile, the Core Ultra 9 285K is better at single-thread performance than the Ryzen 9 9950X3D, where the former exhibits a speed increase of 9% over the latter. It can be argued that a loss of 3% is more tolerable than a loss of 9%; this perspective holds validity when one prioritizes a chip for productivity purposes while overlooking gaming considerations.
Overclocking: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D and Intel Core Ultra 9 285K have unlocked multipliers and are ready for your manual overclocking endeavors. The quality of overclocking can vary significantly between processors, and currently, we do not possess a substantial number of samples from which to derive definitive conclusions. Our results are primarily based on our overclocking experiences with the single sample available in our lab.
In the context of the Ryzen 9 9950X3D, we activated AMD's Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) functionality. For the PBO configuration, we utilized the 'advanced' and 'motherboard' power settings, accompanied by a 10X scalar adjustment and an increase of 200 MHz in the clock speed. Furthermore, we implemented a -15 all-core Curve Optimizer offset.
We've also experimented with Intel's latest '200S Boost' feature combined with some manual overclocking. But the long story short is that there isn't much practical headroom for performance gains with fabric overclocking. Intel also offers manual tuning for the P-cores and E-cores, though the actual performance gains are heavily weighted towards the latter.
⭐ Winner: Tie
Unlike the old Pentium, modern processors arrive with little headroom for serious overclocking with conventional cooling. It's a two-way street. On a positive note, you can rest easy at night knowing their chips are at or near their potential. However, on the downside, the art of extracting additional performance at no cost is slowly fading away.
Power Consumption, Efficiency, and Cooling: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
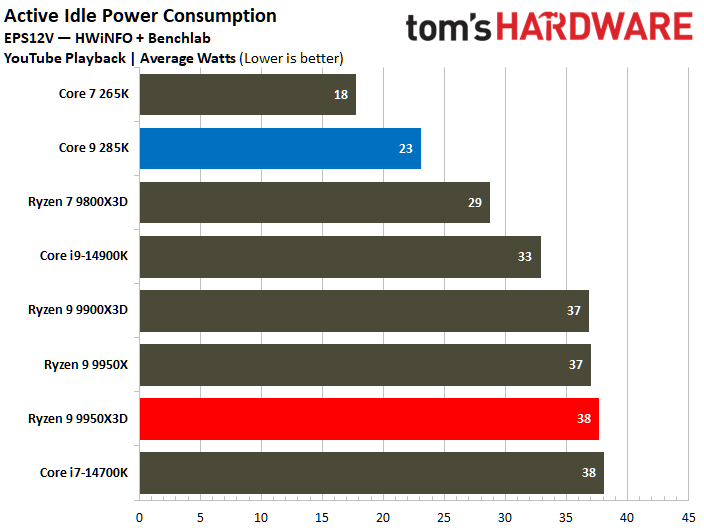
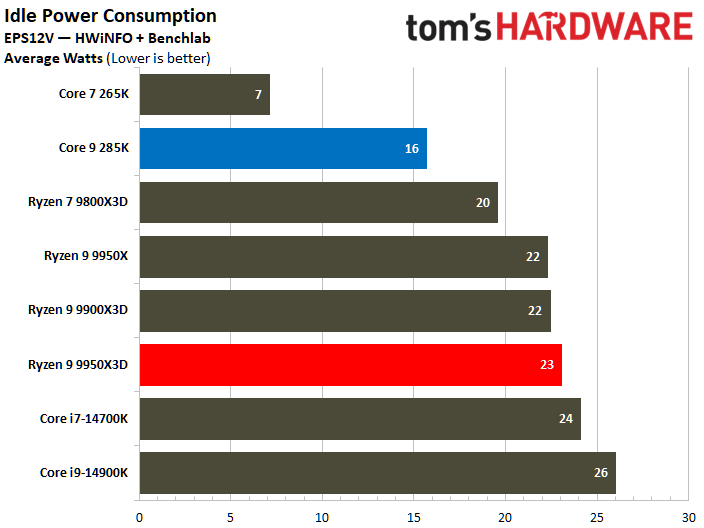
The Core Ultra 9 285K has 30% lower idle power consumption than the Ryzen 9 9950X3D. Furthermore, the Core Ultra 9 285 K's active idle power consumption during YouTube playback is particularly notable, as it consumes 39% less power.
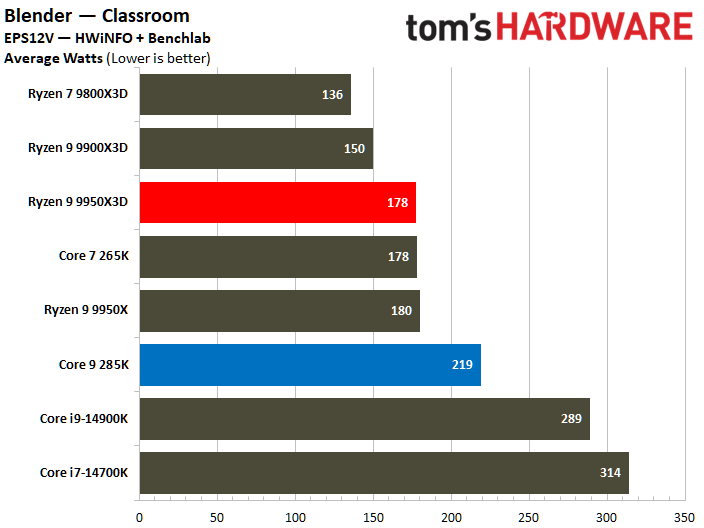
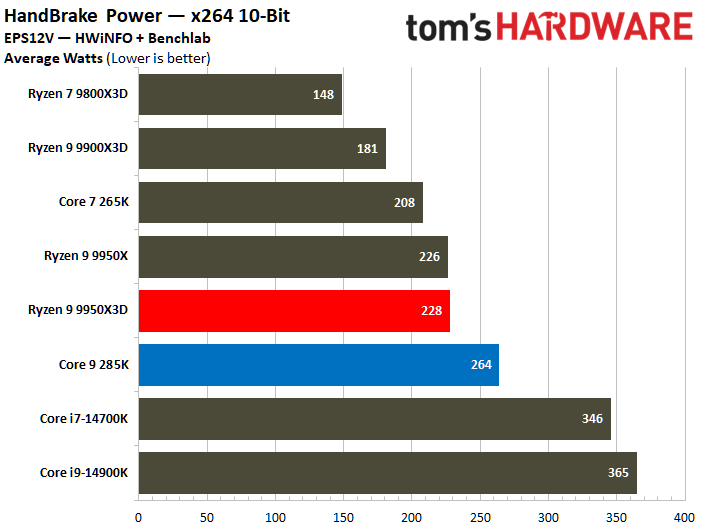
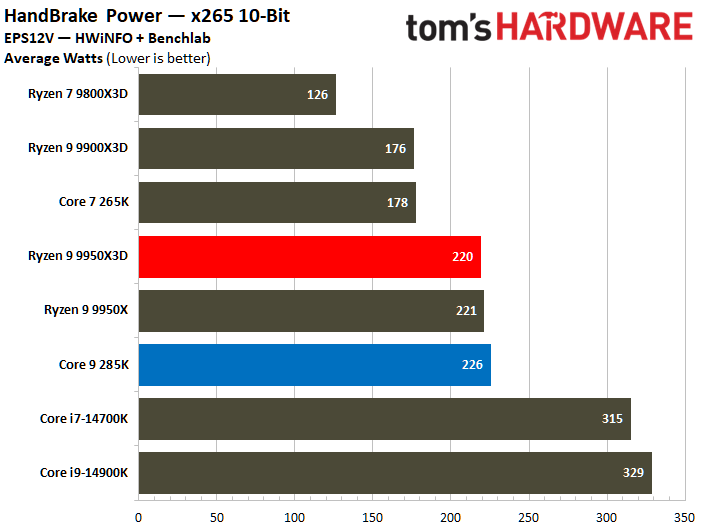
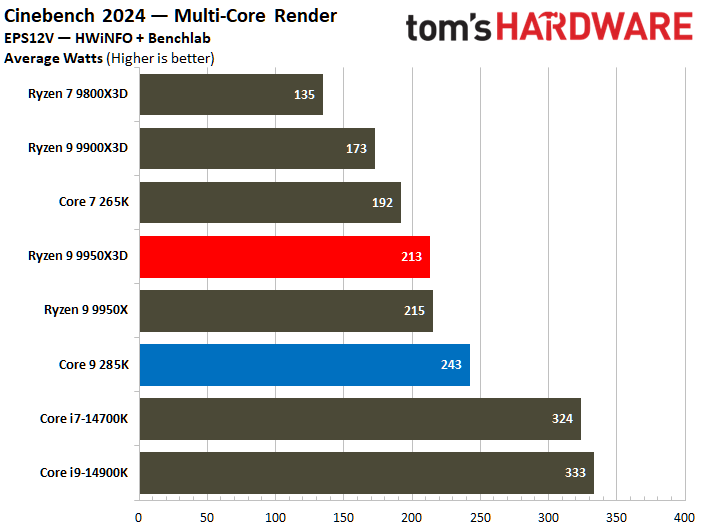
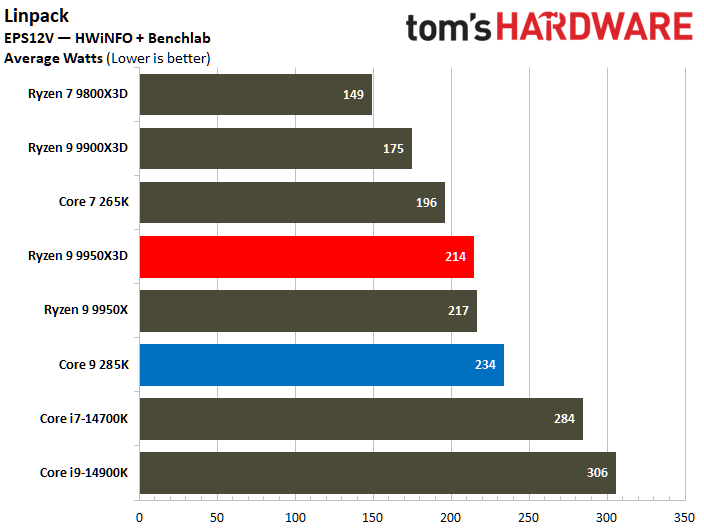
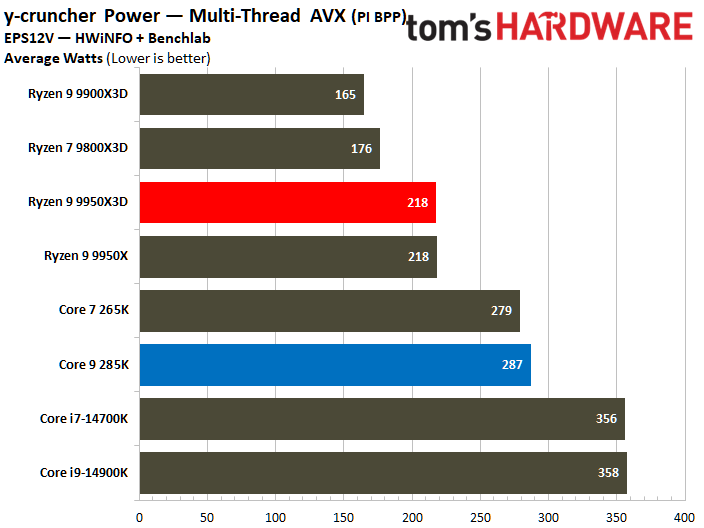
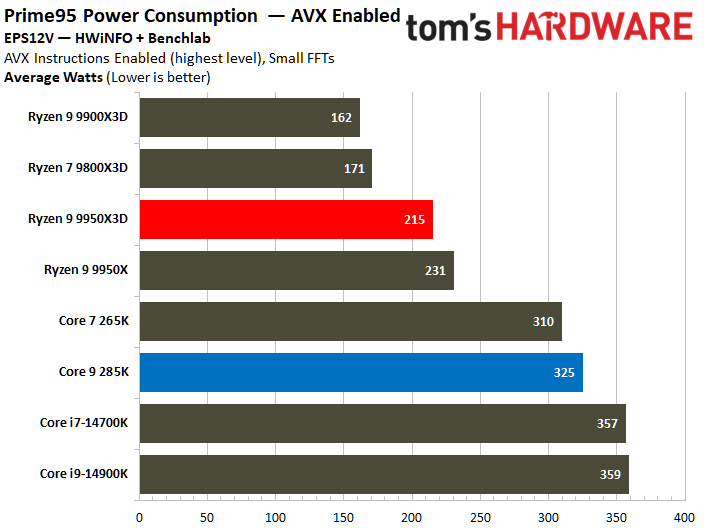
On the contrary, the Core Ultra 9 285K reveals a higher power consumption during various workload scenarios. The Intel chip operates within a power range of 219W to 325W, whereas its AMD counterpart operates between 178W and 228W. Notably, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has a peak power consumption that is 30% lower than that of the Core Ultra 9 285K.
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
(Image credit: Tom's Hardware)
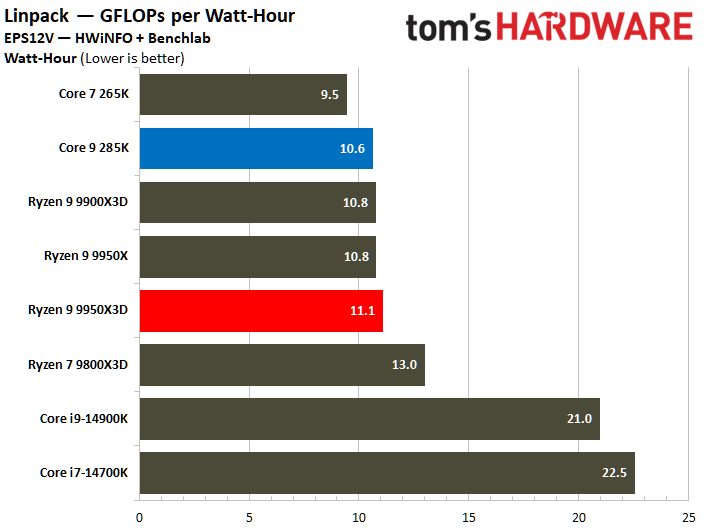
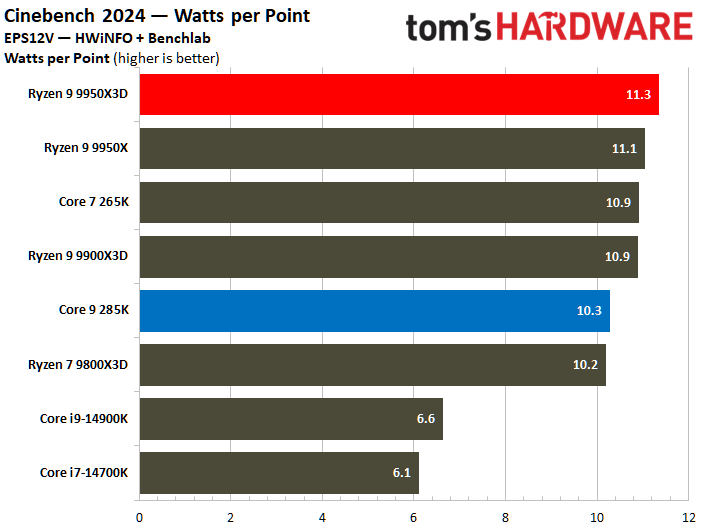
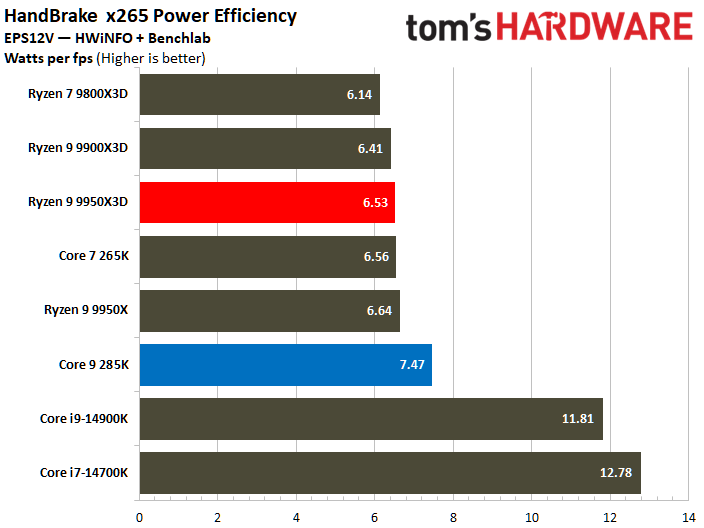
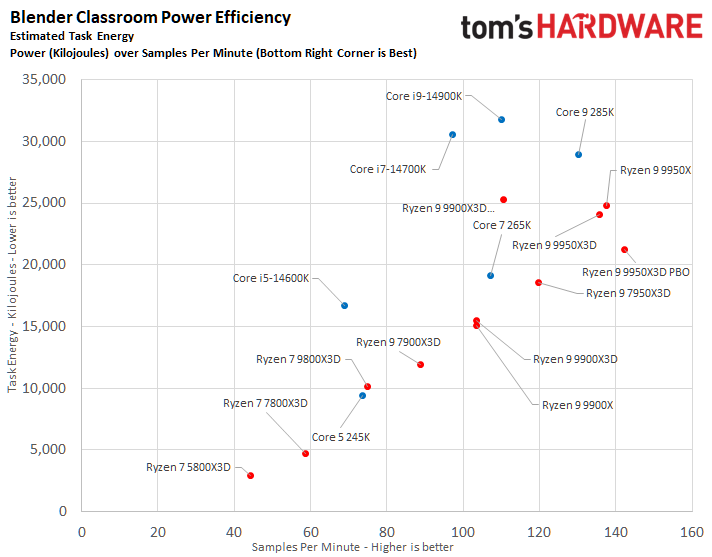
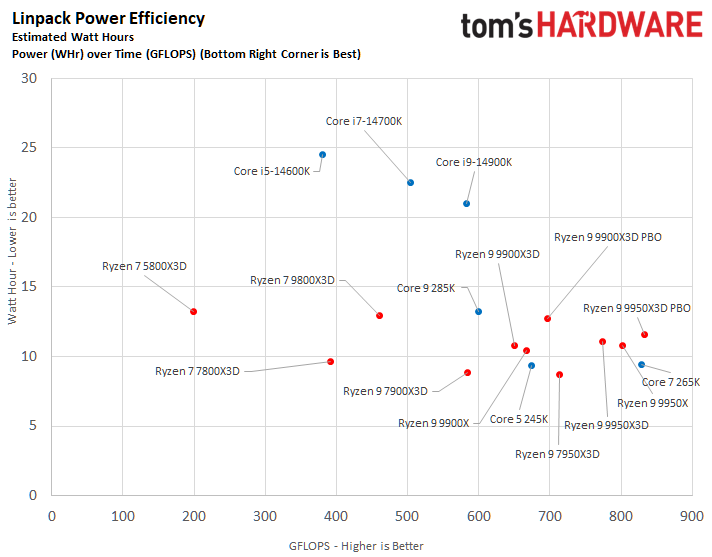
The Core Ultra 9 285K was more power efficient in the Linpack workload, displaying a 5% lower watt-hour. The Ryzen 9 9950X3D excelled in the Cinebench 2024 workload, landing a 10% higher watts per point and a 13% lower watts per FPS in the HandBrake x265 test.
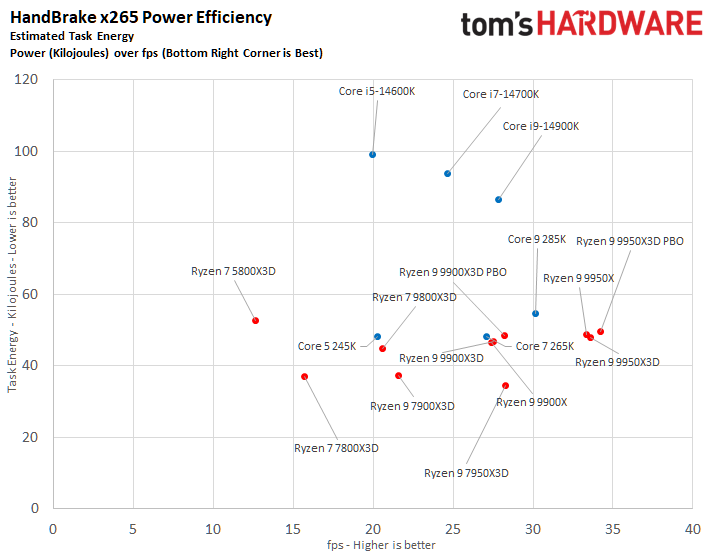
The ideal balance is performance at a reduced power consumption. To elaborate, the processor at the bottom right corner of the power efficiency charts represents the best chip in terms of efficiency. The Ryzen 9 9950X3D outperforms the Core Ultra 9 285K in multiple benchmarks.
⭐ Winner: AMD
The Core Ultra 9 285K wins at idle power consumption, but the Ryzen 9 9950X3D consumes less power. While both idle and average power consumption should be considered, the latter is ultimately more important since we typically use our systems more than letting them idle for prolonged periods.
Furthermore, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has better power efficiency than the Core Ultra 9 285K. A power-efficient processor helps reduce system costs, including processor cooling and power supply capacity expenses. It also positively contributes to electricity savings.
Pricing: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D launched last month at $699. Since this processor recently came out of the oven, it's unrealistic to expect any price adjustments. Meanwhile, the Core Ultra 9 285K debuted at $620 in October 2024. Nowadays, you can find the flagship Arrow Lake chip at U.S. retailers for $589, 5% below the launch price.
Intel processors usually maintain their value until the next generation arrives. Therefore, it's unlikely that the Core Ultra 9 285K will officially get any cheaper. You may still find a retailer deal here or there.
To put things in perspective, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D's gaming performance is 34% higher than the Core Ultra 9 285K while being 19% more expensive. The Zen 5 part has a 3% multi-threaded advantage over the Core Ultra 9 285K, but the Intel chip does have up to 9% higher single-threaded performance, though.
⭐ Winner: AMD
At $699, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D may look like a scary investment. However, our results show that even with that hefty price tag, the 3D V-Cache flagship gives you more value for your money in gaming. The multi-threaded performance isn't shabby, but it does lose out to the Core Ultra 9 285K in single-threaded performance.
The Ryzen 9 9950X3D already looks good. However, its appeal will grow further when the pricing starts to decline, whether through official price reductions or retailer promotions during special events such as Black Friday.
Bottom Line: AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D vs Intel Core Ultra 9 285K
| Header Cell - Column 0 | AMD Ryzen 9 9950X3D | Intel Core Ultra 9 285K |
|---|---|---|
Features and Specifications | ❌ | ❌ |
Gaming | ❌ | Row 1 - Cell 2 |
Productivity Applications | ❌ | ❌ |
Overclocking | ❌ | ❌ |
Power Consumption, Efficiency, and Cooling | ❌ | Row 4 - Cell 2 |
Pricing | ❌ | Row 5 - Cell 2 |
Total | 6 | 3 |
The gaming performance of the Ryzen 9 9950X3D was never in doubt, particularly given that lower-tier Zen 5 components equipped with 3D V-Cache have already surpassed the Core Ultra 9 285K by massive margins. However, the more important question is whether the Ryzen 9 9950X3D possesses any appeal outside the gaming realm. The answer to this inquiry is yes.
In addition to being a great gaming processor, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D can double as a productivity monster, similar to the vanilla Ryzen 9 9950X. Thanks to the Zen 5 architecture and the 16-core, 32-thread configuration, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D has no issues tackling demanding workloads, as long as they benefit from multi-threading. Unfortunately, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D's single-threaded performance lags behind the Core Ultra 9 285K.
However, if you can overlook the Ryzen 9 9950X3D's single-threaded weakness, the Zen 5 chip is a fantastic all-around performer that's power efficient and offers support for the latest technology. And unlike the Core Ultra 9 285K, the Ryzen 9 9950X3D doesn't leave you feeling like you just bought an obsolete processor—at least for a couple of years.

-
 C114 Communication Network
C114 Communication Network -
 Communication Home
Communication Home


